DECORATION
Τ he ancient Greek temple was a dedication to the deity and therefore it had to be perfect of form and decorated with works of art. Thus, already from the Early Archaic period, the lavish external decoration of temples, which offered nothing to their function, was of great visual artistic interest.
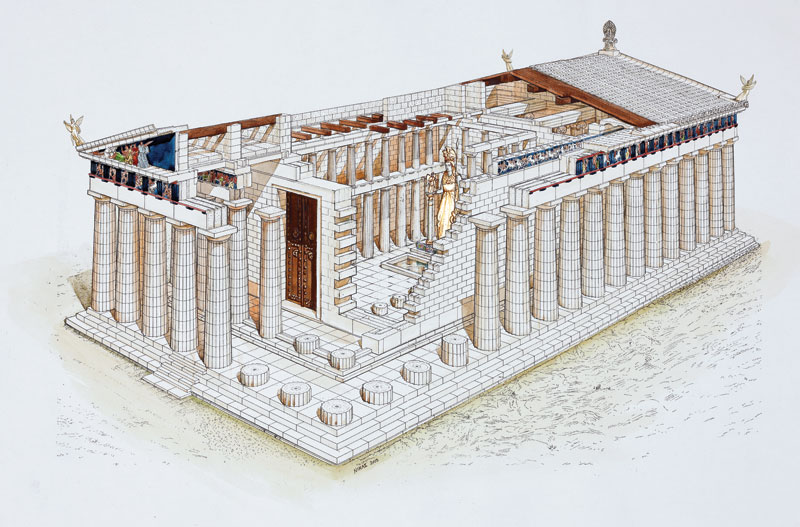
PEDIMENTS - IONIC AND DORIC FRIEZE
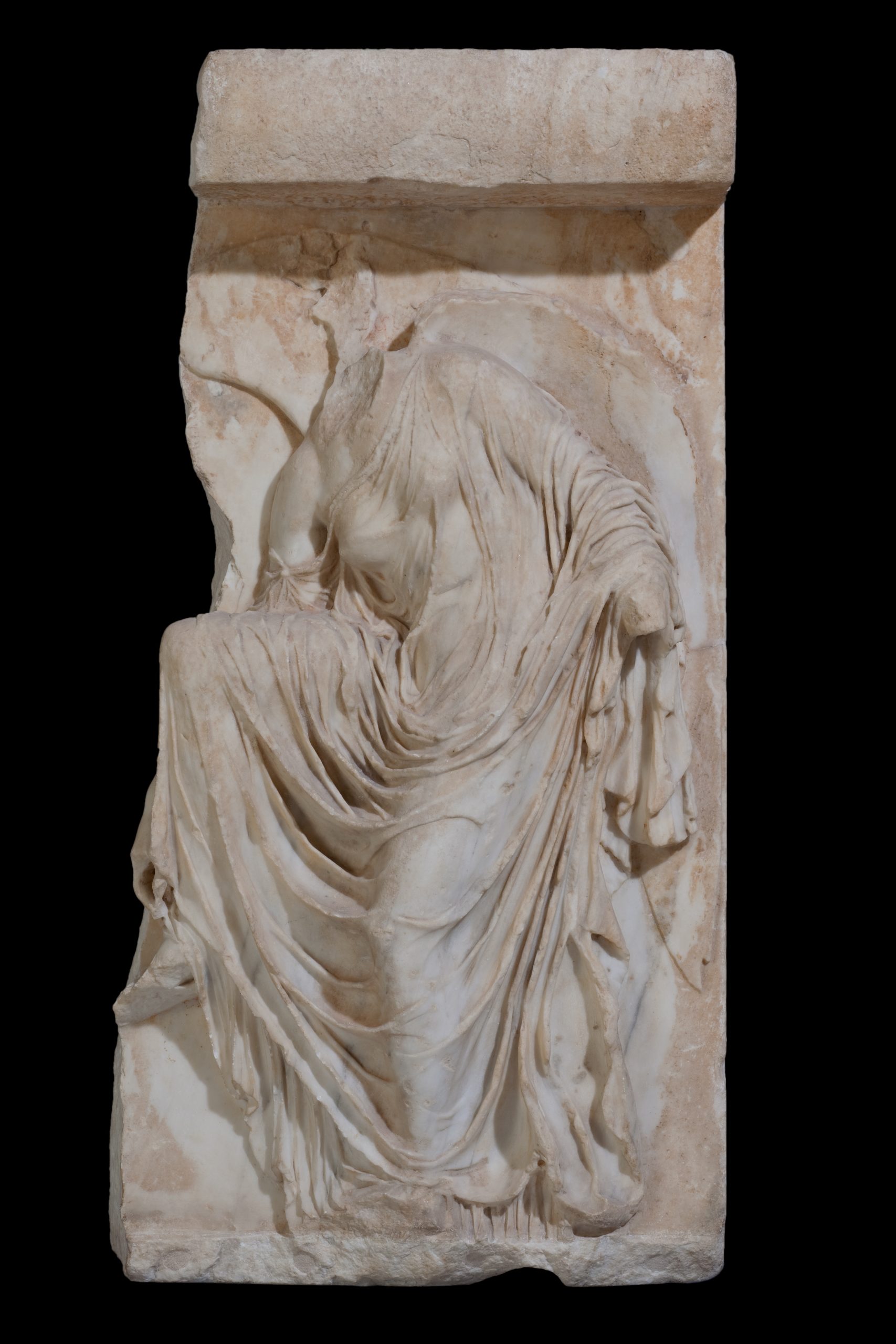
I n Late Archaic and Classical times, temples were decorated with statues and reliefs, mainly in marble. The sculpted decoration was also a dedication to the god, and therefore perfect in form and workmanship, even in those parts that were practically hidden from view. The larger than life-size pedimental statues sculpted by Pheidias for the Parthenon, the back of which is superbly beautiful yet was unseen, are a well-known example.




Τ he subjects of the compositions on the pediments and the reliefs of the friezes of both the Ionic and Doric temples drew on myths associated with the honoured god or on mythology in general. Struggles were frequently represented, such as the battle with Centaurs (Centauromachy), the battle with Amazons (Amazonomachy), the battle with Giants (Gigantomachy), as on the temple of Zeus at Olympia, the temple of Aphaia on Aegina and the Archaic temples on the Acropolis. The metopes had comparable themes.
The continuous frieze was an element of the Ionic order, which was also used exceptionally on Doric temples in Classical times, such as the Parthenon, the temple of Apollo Epicourios at Bassae and the temple of Hephaistos in Athens (the so-called "Theseion"). Famed in the history of ancient art is the frieze that surrounded the cella, the pronaos and the opisthonaos of the Parthenon, the subject of which was the Panathenaic procession to the Acropolis.

OTHER SCULPTURES
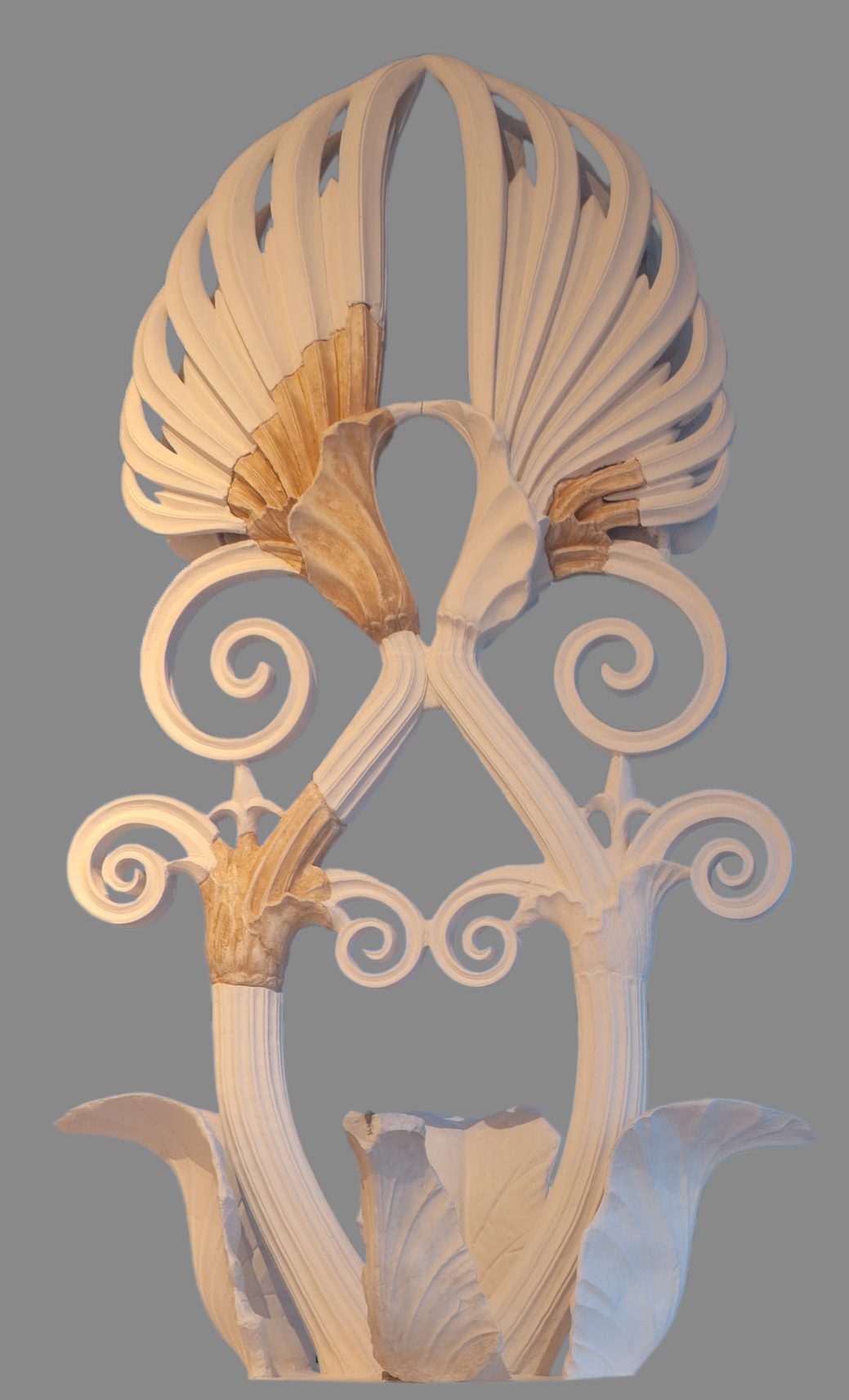

O n the top of the angles of the pediments stood the acroteria, of geometric shapes on the early monuments, of vegetal forms later, free-standing statues during the Classical period. The acroteria of vegetal form were large composite palmettes at the apex and half-palmettes at the two side angles. The statues in the round were usually female, Nikai (Victories), Nymphs or Nereids, in various groups.
The coffers of the marble ceilings also bore sculpted decoration of flowers or palmettes projecting in the recess, made of bronze, as in the Erectheion, which have not survived, or of marble, as in the Tholos at the sanctuary of Asklepios at Epidaurus as well as in many later monuments.


The mouldings (cymatia) were linear relief, usually horizontal elements whose purpose was to articulate the surfaces of the façades. Three kinds are distinguished, on the basis of their decoration: Doric, Ionic and Lesbian. Antae capitals and "epicranitis" zones were also formed of cymatia, as for example on the Erechtheion.
The altars and the pedestals of cult statues, and other features such as the parapets around the temple of Athena Nike, were also sometimes decorated with reliefs. It goes without saying that the decoration was completely attuned to the overall sculpted impression of the architecture of the temple when seen in the sunlight and was achieved with the contribution of all the morphological features of a temple.

COLOUR DECORATION
C olour and painted decoration were part of the ancient architecture, completing a monument's visual effect. The present golden hue of the marble is due to age. But when the marble buildings were under construction their appearance was different, since newly cut marble would have shone dazzlingly in the sun. Immediately following, certain of the white surfaces would have been covered in various rich colours. The precise allocations of these colours is unknown to us.


Nevertheless, it seems that the following colours were used:
Bases, columns and architrave: off white
Tainia: red with golden meander
Regula: dark blue with golden anthemia
Mutule: blue
Triglyphs and background of metopes: alternate blue and red
Background of pediments and background of frieze: blue
Cymatia, astragaloi, coffers, antefixes: a combination of red, blue, yellow, green and golden
Sculptures: polychrome with gilded bronze fittings
